Installation¶
Prerequisite¶
- A database (MariaDB/Mysql or Postgres) accessible to both your Salt master and Alcali.
- the Salt-Api installed and accessible by Alcali.
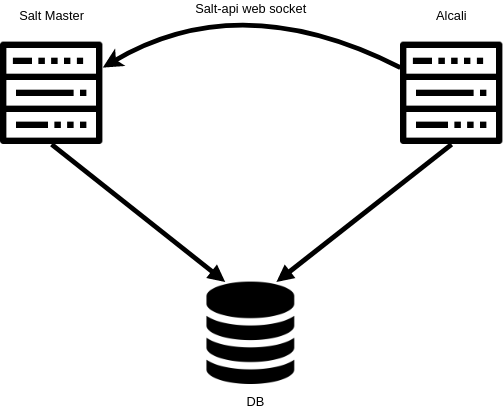
Preparing the salt master¶
Database access and master job store configuration¶
The salt master needs to store its jobs on the chosen database.
Warning
Don't forget to install database connectors:
python-mysqldb/python3-mysqldbfor MySQL/MariaDBpython-psycopg2/python3-psycopg2for Postgres
MySQL/MariaDB schema and configuration example
CREATE DATABASE `salt`
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8
DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE `salt`;
--
-- Table structure for table `jids`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `jids`;
CREATE TABLE `jids` (
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`load` mediumtext NOT NULL,
UNIQUE KEY `jid` (`jid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_returns`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_returns`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_returns` (
`fun` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`jid` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`return` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`success` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`full_ret` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
KEY `id` (`id`),
KEY `jid` (`jid`),
KEY `fun` (`fun`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
--
-- Table structure for table `salt_events`
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `salt_events`;
CREATE TABLE `salt_events` (
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`tag` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`data` mediumtext NOT NULL,
`alter_time` TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`master_id` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `tag` (`tag`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
event_return: [mysql]
master_job_cache: mysql
mysql.host: 'db'
mysql.user: 'alcali'
mysql.pass: 'alcali'
mysql.db: 'salt'
mysql.port: 3306
Postgres commands and configuration example
psql << EOF
CREATE ROLE salt WITH PASSWORD 'salt';
CREATE DATABASE salt WITH OWNER salt;
EOF
psql -h localhost -U salt << EOF
--
-- Table structure for table 'jids'
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS jids;
CREATE TABLE jids (
jid varchar(20) PRIMARY KEY,
load text NOT NULL
);
--
-- Table structure for table 'salt_returns'
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS salt_returns;
CREATE TABLE salt_returns (
fun varchar(50) NOT NULL,
jid varchar(255) NOT NULL,
return text NOT NULL,
full_ret text,
id varchar(255) NOT NULL,
success varchar(10) NOT NULL,
alter_time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE INDEX idx_salt_returns_id ON salt_returns (id);
CREATE INDEX idx_salt_returns_jid ON salt_returns (jid);
CREATE INDEX idx_salt_returns_fun ON salt_returns (fun);
CREATE INDEX idx_salt_returns_updated ON salt_returns (alter_time);
--
-- Table structure for table 'salt_events'
--
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS salt_events;
DROP SEQUENCE IF EXISTS seq_salt_events_id;
CREATE SEQUENCE seq_salt_events_id;
CREATE TABLE salt_events (
id BIGINT NOT NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT nextval('seq_salt_events_id'),
tag varchar(255) NOT NULL,
data text NOT NULL,
alter_time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT NOW(),
master_id varchar(255) NOT NULL
);
CREATE INDEX idx_salt_events_tag on salt_events (tag);
EOF
event_return: [postgres]
master_job_cache: postgres
returner.postgres.host: 'db'
returner.postgres.user: 'alcali'
returner.postgres.passwd: 'alcali'
returner.postgres.db: 'salt'
returner.postgres.port: 5432
By default, jobs are only kept for 24 hours. Set keep_jobs: 0 to disable the cache cleaner (see managing the job cache).
Returners provide a way to archive old jobs. Refer to Salt MySQL or Postgres returner documentation for more information.
Salt Api¶
Salt master configuration example:
rest_cherrypy:
port: 8080
host: 0.0.0.0
debug: True
ssl_crt: /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt
ssl_key: /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.key
Install instruction example (On Debian 9 using Salt python3 version):
apt-get install -y salt-api python3-openssl
salt-call --local tls.create_self_signed_cert cacert_path='/etc/pki'
Please refer to Salt rest_cherrypy documentation for more infos on how to setup the salt-api.
Authentication¶
Alcali provide two authentication methods:
- a rest endpoint on alcali.
- a custom token based auth module for Salt.
Rest endpoint authentication¶
To use the rest endpoint authentication, the salt master must be able to connect to alcali.
Set SALT_AUTH=rest in the env file and use the rest external auth in the salt master configuration.
the ^url key is how the salt master connect to alcali.
external_auth:
rest:
^url: http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/token/verify/
admin:
- .*
- '@runner'
- '@wheel'
Custom token auth module¶
Set SALT_AUTH=alcali in the env file
You can get the Alcali auth module here
Place it on the salt filesystem (for example: /srv/salt/auth) and add it to your Salt master configuration:
auth_dirs: [/srv/salt/auth]
External auth example:
eauth_acl_module: alcali
keep_acl_in_token: true
external_auth:
alcali:
admin:
- .*
- '@runner'
- '@wheel'
Don't forget to run salt-run saltutil.sync_all on the salt master.
See Saltstack external auth system for more infos.
Tokens can be managed using the alcali command or directly in the web interface.
Installing Alcali¶
The easiest way to install Alcali is to use the Salt Formula
Info
Alcali follow Salt major and minor versioning.
If you are using 2019.2.X Salt version, you should install 2019.2.X Alcali version.
Otherwise, there are 3 different ways to install Alcali manually:
- Using a docker container
- From PyPI
- From Sources
Using Docker¶
The official Docker image for Alcali comes with all dependencies pre-installed and ready-to-use with the latest version published on PyPI. Pull it with:
# you can specify which version: latenighttales/alcali:2018.3.2
docker pull latenighttales/alcali:latest
The alcali executable is provided as an entrypoint.
Locally¶
To install Alcali locally, you'll need to install database connectors dependencies:
For Debian based distribution:
# For postgres database
apt install libpq-dev gcc
# For mariadb database
apt install libmariadbclient-dev gcc
For Red-Hat based distribution:
# For postgres database
yum install libpq-devel gcc
# For mariadb database
yum install mysql-devel gcc
Install from PyPI¶
Warning
We strongly recommend installing Alcali in a virtualenv.
Example:
python3 -m venv $HOME/.venv
source $HOME/.venv/bin/activate
Simply do:
pip install --user alcali
And for mysql/mariadb:
pip install --user mysqlclient
or for postgres:
pip install --user psycopg2
Install from Sources¶
git clone https://github.com/latenighttales/alcali.git
git checkout 2019.2 # or 2018.3
pip install --user .
And for mysql/mariadb:
pip install --user mysqlclient
or for postgres:
pip install --user psycopg2
Installation with LDAP support¶
if you want to use LDAP to authenticate users, you'll need these system dependencies:
For Debian based distribution:
apt install libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev ldap-utils
For Red-Hat based distribution:
yum install openldap-devel
To add LDAP support to alcali, just append [ldap] to the chosen install method i.e:
# Install from PyPI
pip install --user alcali[ldap]
# Install from Source
pip install --user .[ldap]
Installation with Google OAuth2 support¶
To add Google OAuth2 support to alcali, just append [social] to the chosen install method i.e:
# Install from PyPI
pip install --user alcali[social]
# Install from Source
pip install --user .[social]