Walkthrough¶
After you logged in at http://localhost:8000/#/login with:
username: admin
password: password
You should land on the Dashboard view.
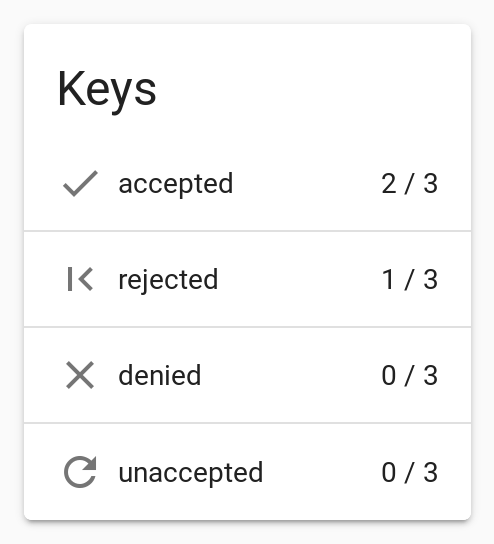
For now it's empty, but you can already see that some keys are UNACCEPTED.
So let's go to the Keys view: http://localhost:8000/#/keys
Accept keys¶
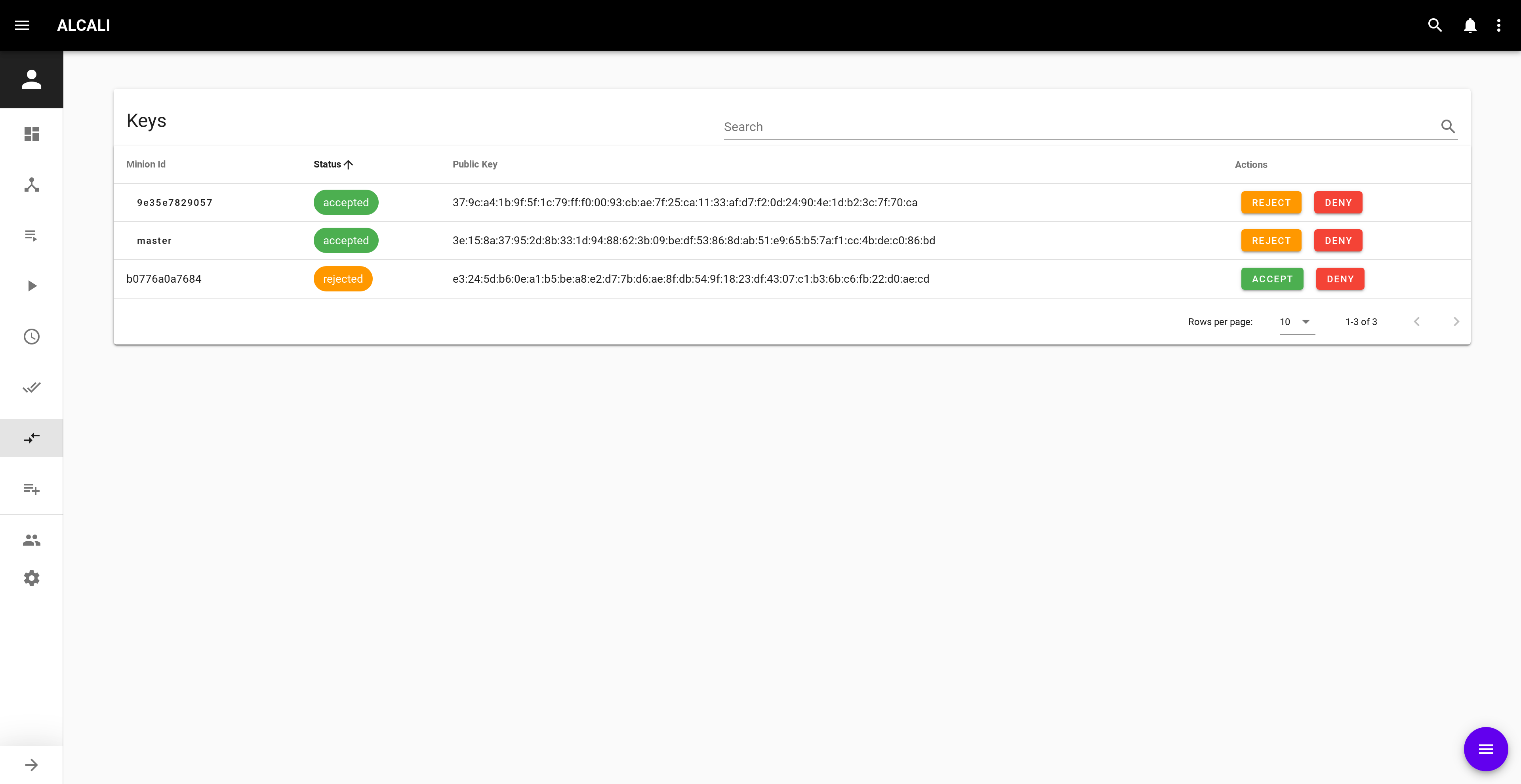
You can either accept keys one by one using the ACCEPT button, or use the action button ![]() to accept all keys.
to accept all keys.
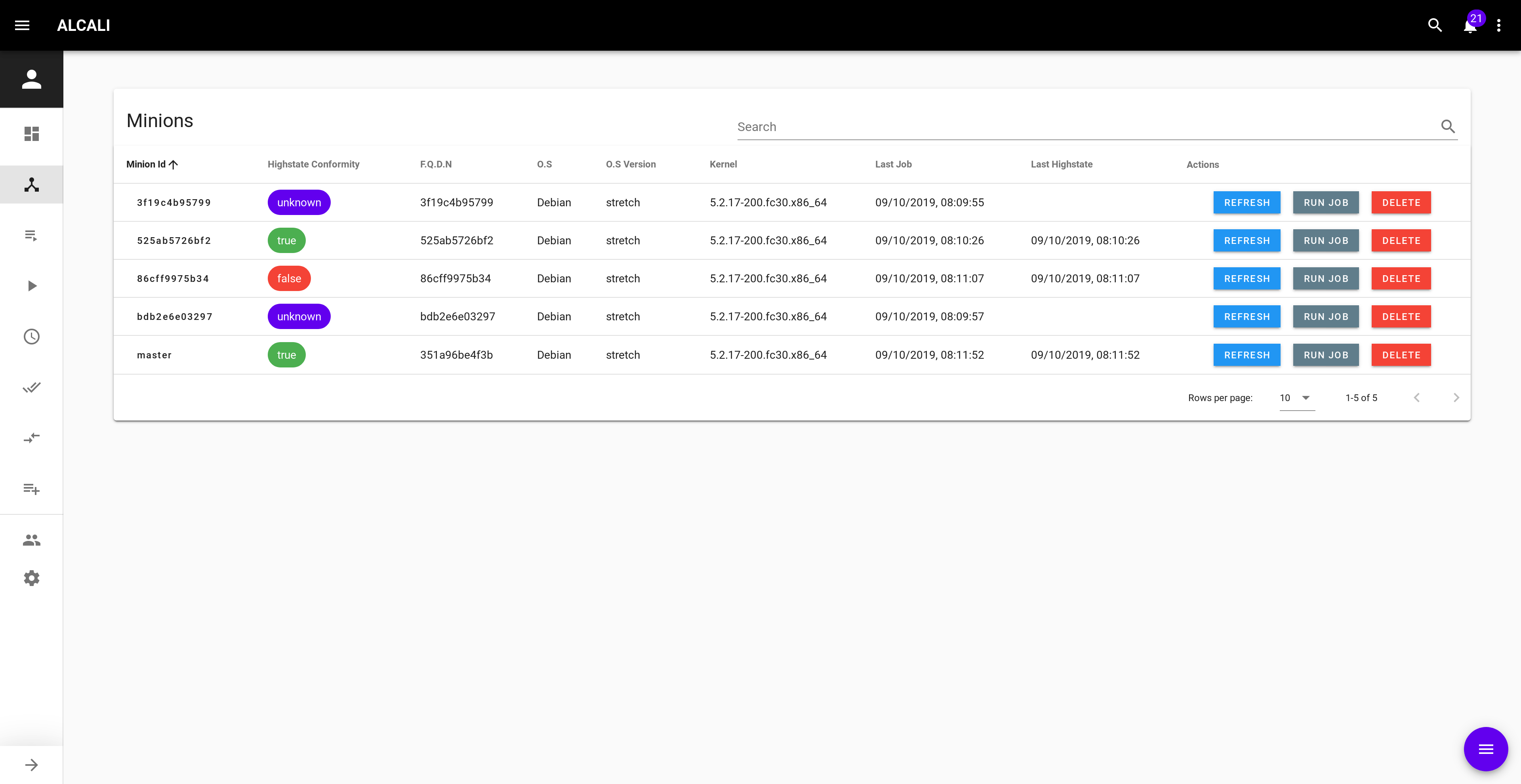
Add minions¶
To store infos on connected minions, we need to add them to the database.
Go to http://localhost:8000/#/minions and use the action button ![]() to refresh minions.
to refresh minions.
Info
By default, refreshing minions will run:
test.pinggrains.itemspillar.items
on each connected minions.
Minion detail¶
From the minions view, you can click on a minion id to see its details, for example: http://localhost:8000/#/minions/master/.
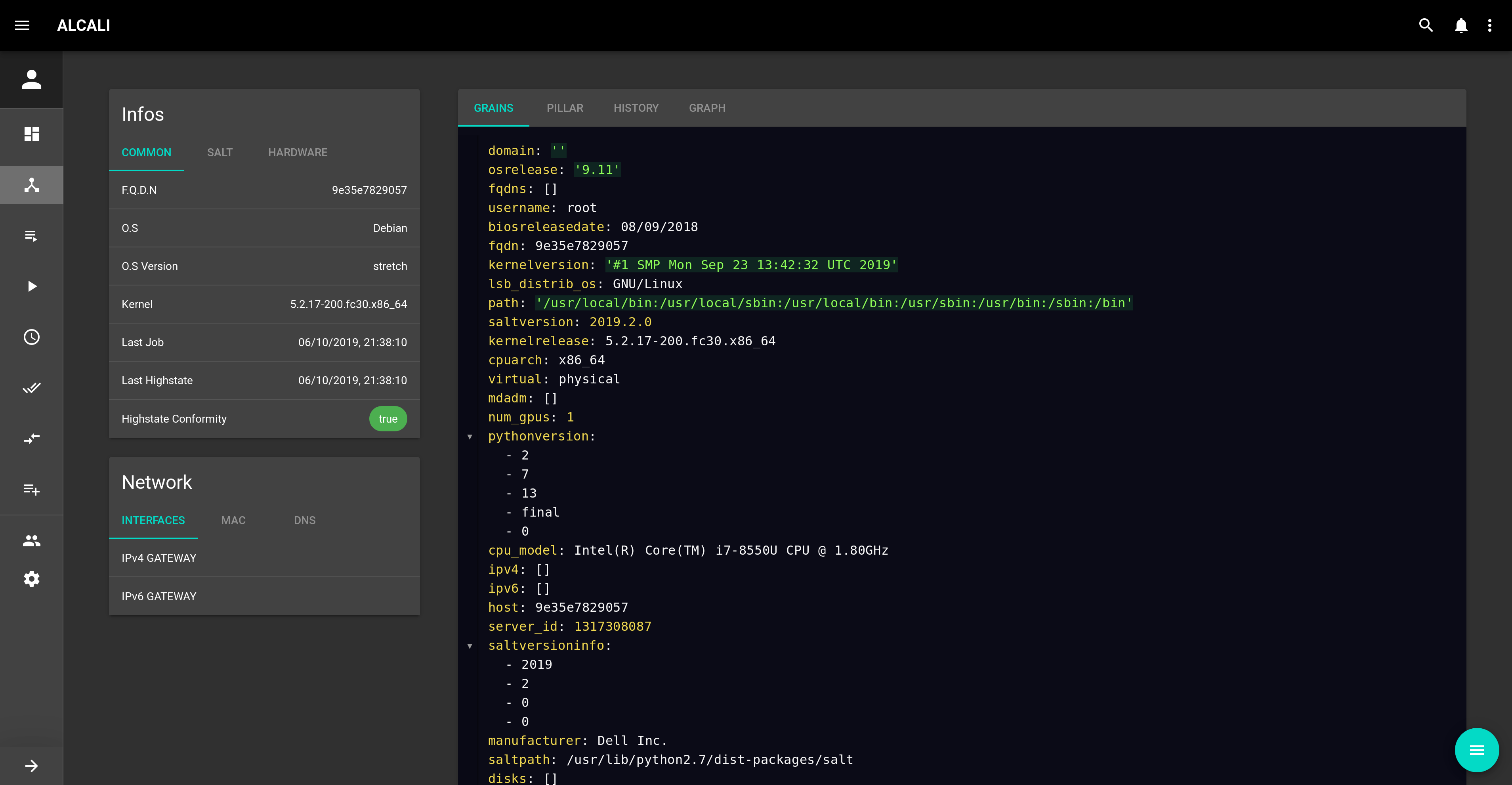
Details are parsed from the grains.items state. On the right, 4 tabs are present for now:
grains.itemspillar.items- The last 100 jobs run on this minion
- A graph of jobs run on this minion
Let's add some useful infos by setting some minions fields. To do so, go to the settings view http://localhost:8000/#/settings.
Settings¶
Choose a target and run the module parser to have documentation and module completion.
Let's add some minion fields.
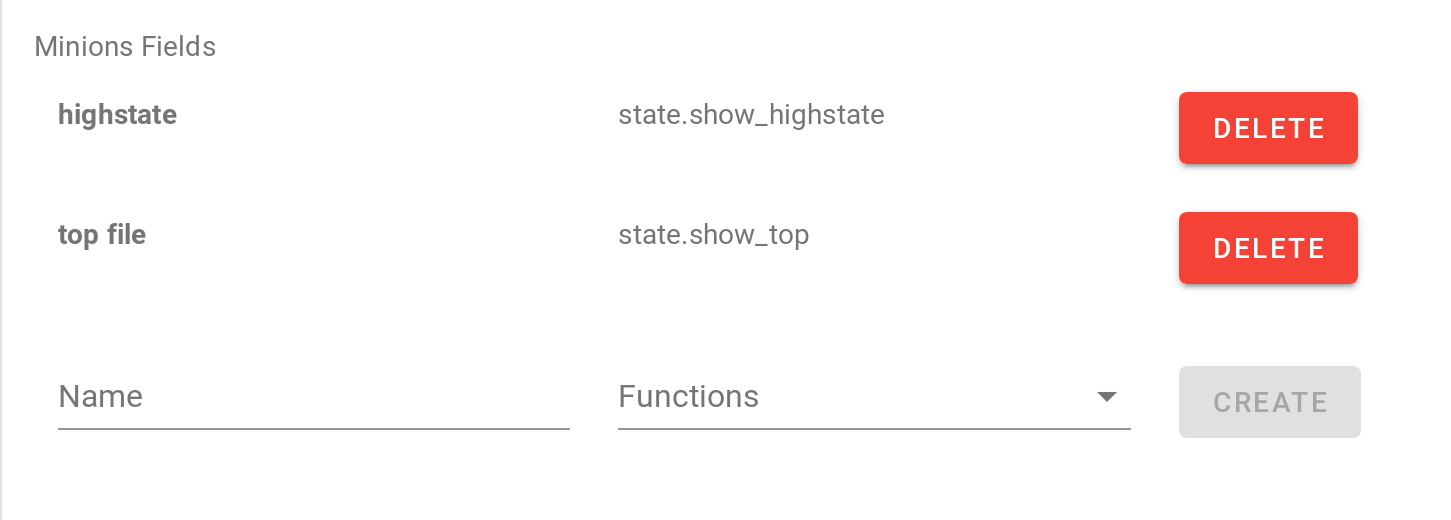
We usually add:
-
highstate:
state.show_highstate -
top file:
state.show_top
Use the action button to refresh all minions.
If you go see a minion's details, for example, http://localhost:8000/#/minions/master/, the new minion fields should be present.
Minion fields are usually used for "static" minion specific data.
For dynamic data, there's conformity.
As a config management tool, it's important to track state of files presence, software version, etc...
Custom conformity let you do that.

As an example, we'll add:
-
foo:
file.file_exists /foo.txt -
pyversion:
cmd.run "python --version"
If you go to the overview, the two new custom conformity should be present but empty.
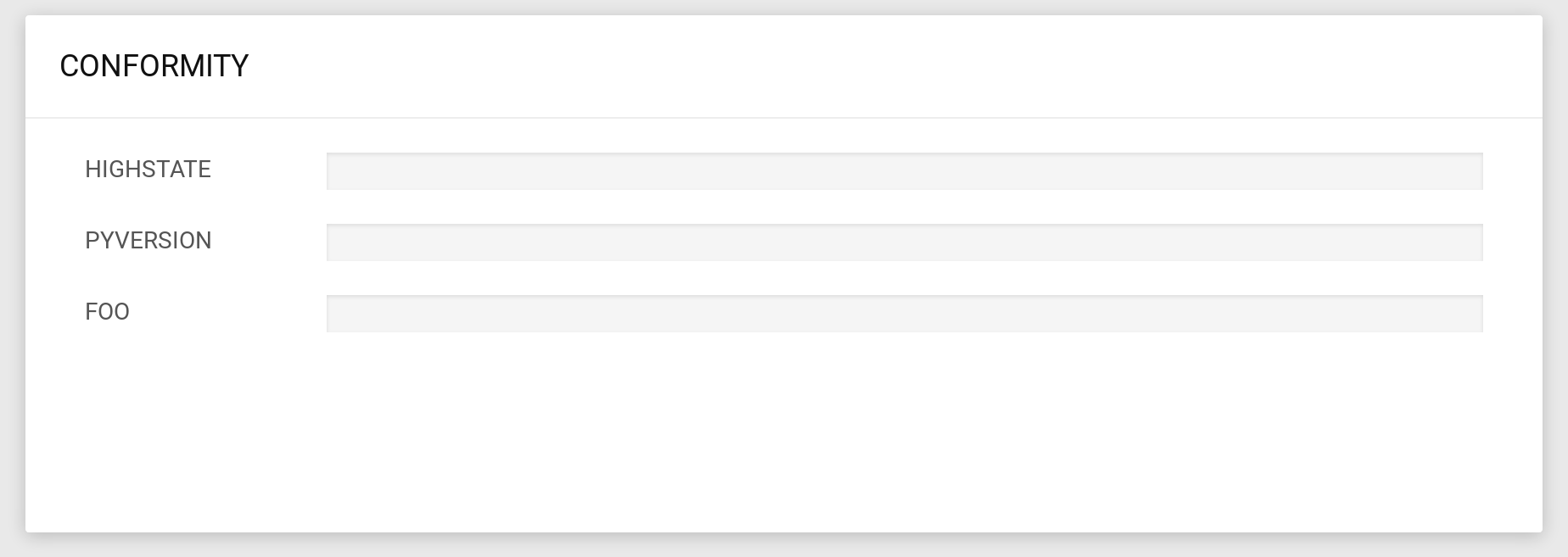
Let's go run some jobs to fix that.
Run¶
Go to http://localhost:8000/#/run
You can explore the formatted tab or just use the cli and run:
salt master cmd.run "touch /foo.txt"
We just created the file /foo.txt on the master, so the master will comply to the "foo" conformity we added earlier.
Conformity is parsed from the states present in the database, so let's run:
salt * cmd.run "python --version"
salt * file.file_exists "/foo.txt"
By the way, there should be tab completion in the CLI and documentation in the tooltip on the formatted tab thanks to the parse module action we did earlier.
Finally, highstate any or all minions.
salt master state.apply
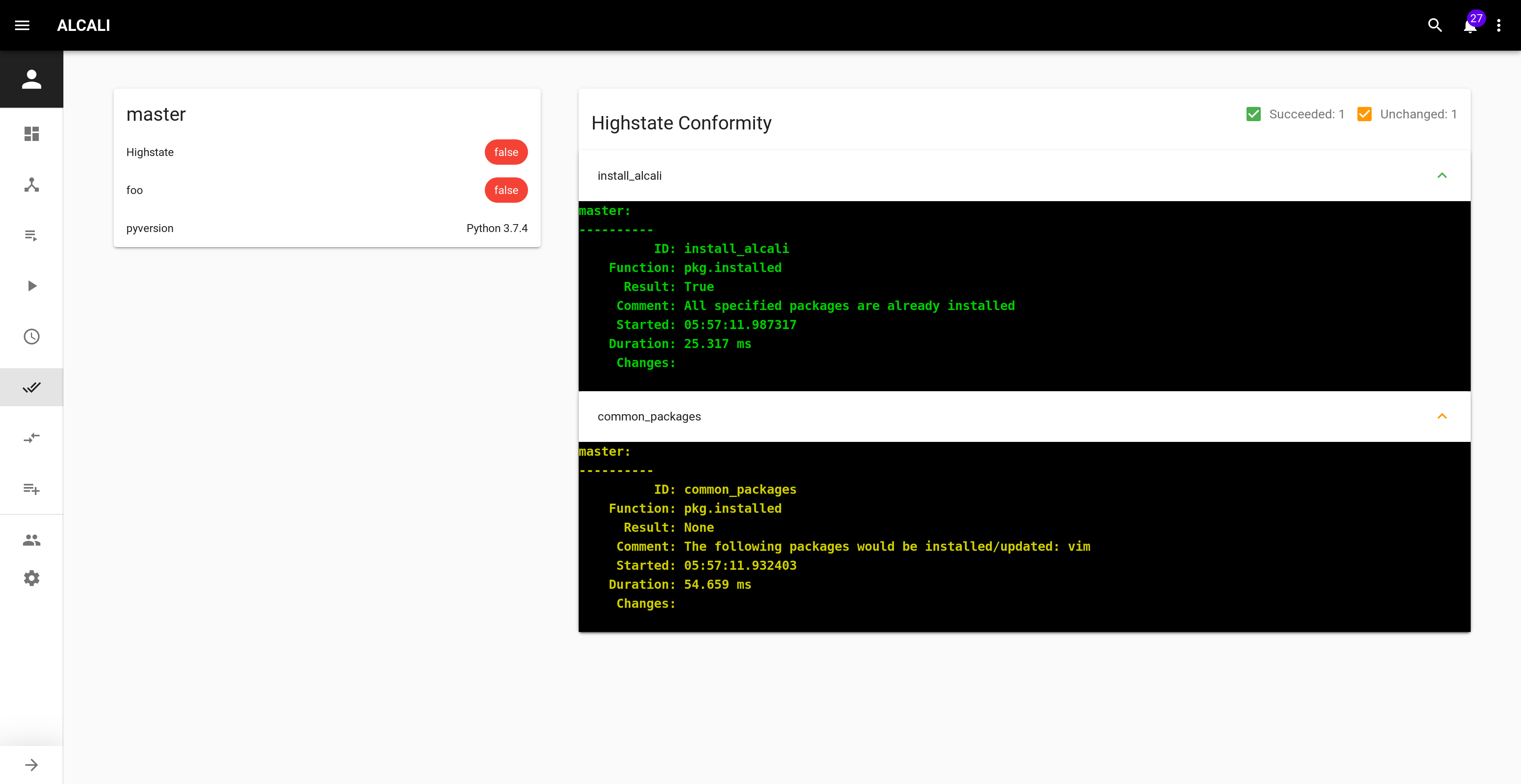
Conformity¶
In the overview, the conformity card should be filled now, with details when you hover it.
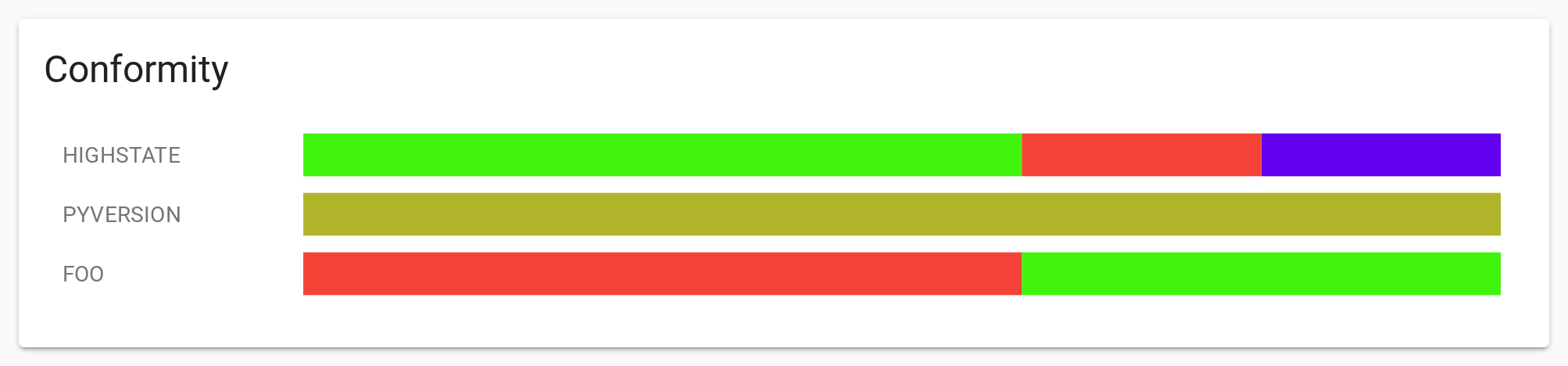
A table with both highstate conformity and your custom ones for all minions is available in the conformity view http://localhost:8000/#/conformity.
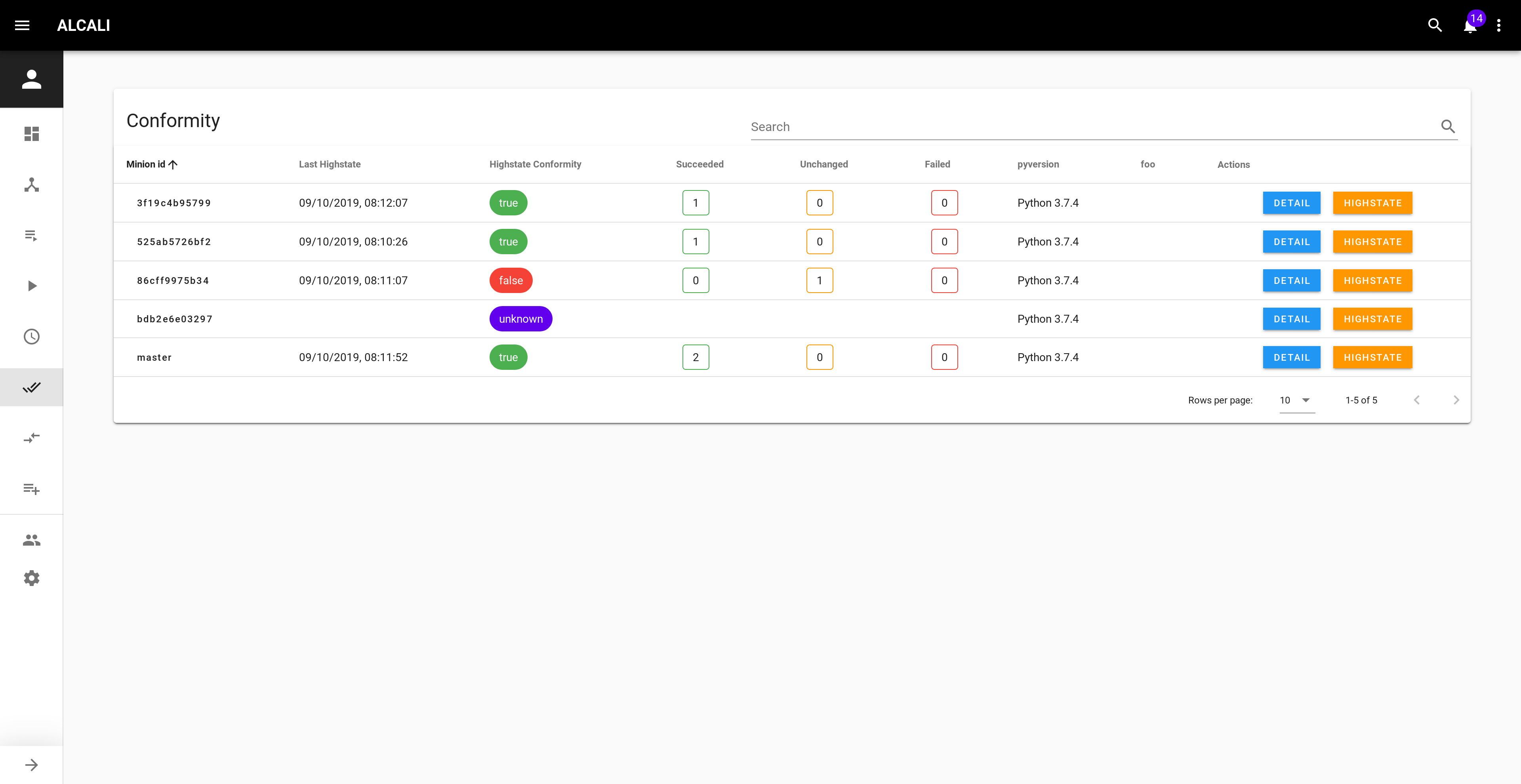
Details about each states in the highstate are available by clicking the DETAIL button.